执行并行流时,它在公共ForkJoinPool(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())中运行,由所有其他并行流共享。
有时我们希望在一个单独的专用线程池上并行执行代码,该线程池由特定数量的线程构成。例如,当使用myCollection.parallelStream()时,它并没有为我们提供方便的方法。
我编写了一个小的实用工具(ThreadExecutor类),可以用于此目的。
在下面的示例中,我将演示ThreadExecutor实用程序的简单用法,用计算出的数字填充一个长数组,每个数字在ForkJoinPool(不是公共池)上的一个线程中计算。
线程池的创建由实用程序完成。我们控制池中线程的数量(int parallelism)、池中线程的名称(在调查线程转储时很有用)以及可选的超时限制。
我用junit5测试了它,它提供了一种很好的方法来计时测试方法。
GitHub中提供了所有源代码,网址为:
https://github.com/igalhaddad/thread-executor
ThreadExecutor实用程序类:
import com.google.common.base.Throwables;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.ExecutionError;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.UncheckedExecutionException;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.UncheckedTimeoutException;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class ThreadExecutor {
public static <T, R> R execute(int parallelism, String forkJoinWorkerThreadName, T source, Function<T, R> parallelStream) {
return execute(parallelism, forkJoinWorkerThreadName, source, 0, null, parallelStream);
}
public static <T, R> R execute(int parallelism, String forkJoinWorkerThreadName, T source, long timeout, TimeUnit unit, Function<T, R> parallelStream) {
if (timeout < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid timeout " + timeout);
// see java.util.concurrent.Executors.newWorkStealingPool(int parallelism)
ExecutorService threadPool = new ForkJoinPool(parallelism, new NamedForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory(forkJoinWorkerThreadName), null, true);
Future<R> future = threadPool.submit(() -> parallelStream.apply(source));
try {
return timeout == 0 ? future.get() : future.get(timeout, unit);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
future.cancel(true);
threadPool.shutdownNow();
Throwable cause = e.getCause();
if (cause instanceof Error)
throw new ExecutionError((Error) cause);
throw new UncheckedExecutionException(cause);
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
future.cancel(true);
threadPool.shutdownNow();
throw new UncheckedTimeoutException(e);
} catch (Throwable t) {
future.cancel(true);
threadPool.shutdownNow();
Throwables.throwIfUnchecked(t);
throw new RuntimeException(t);
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
public static <T> void execute(int parallelism, String forkJoinWorkerThreadName, T source, Consumer<T> parallelStream) {
execute(parallelism, forkJoinWorkerThreadName, source, 0, null, parallelStream);
}
public static <T> void execute(int parallelism, String forkJoinWorkerThreadName, T source, long timeout, TimeUnit unit, Consumer<T> parallelStream) {
if (timeout < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid timeout " + timeout);
// see java.util.concurrent.Executors.newWorkStealingPool(int parallelism)
ExecutorService threadPool = new ForkJoinPool(parallelism, new NamedForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory(forkJoinWorkerThreadName), null, true);
CompletableFuture<Void> future = null;
try {
Runnable task = () -> parallelStream.accept(source);
if (timeout == 0) {
future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(task, threadPool);
future.get();
threadPool.shutdown();
} else {
threadPool.execute(task);
threadPool.shutdown();
if (!threadPool.awaitTermination(timeout, unit))
throw new TimeoutException("Timed out after: " + Duration.of(timeout, unit.toChronoUnit()));
}
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
threadPool.shutdownNow();
throw new UncheckedTimeoutException(e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
future.cancel(true);
threadPool.shutdownNow();
Throwable cause = e.getCause();
if (cause instanceof Error)
throw new ExecutionError((Error) cause);
throw new UncheckedExecutionException(cause);
} catch (Throwable t) {
threadPool.shutdownNow();
Throwables.throwIfUnchecked(t);
throw new RuntimeException(t);
}
}
}NamedForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory类:
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinWorkerThread;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class NamedForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory implements ForkJoinPool.ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory {
private AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final String name;
private final boolean daemon;
public NamedForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory(String name, boolean daemon) {
this.name = name;
this.daemon = daemon;
}
public NamedForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory(String name) {
this(name, false);
}
@Override
public ForkJoinWorkerThread newThread(ForkJoinPool pool) {
ForkJoinWorkerThread t = ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory.newThread(pool);
t.setName(name + counter.incrementAndGet());
t.setDaemon(daemon);
return t;
}
}ThreadExecutorTests单元测试类:
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import com.github.igalhaddad.threadexecutor.timing.TimingExtension;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@ExtendWith(TimingExtension.class)
@TestMethodOrder(OrderAnnotation.class)
@DisplayName("Test ThreadExecutor utility")
public class ThreadExecutorTests {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(ThreadExecutorTests.class.getName());
private static final int SEQUENCE_LENGTH = 1000000;
private static List<long[]> fibonacciSequences = new ArrayList<>();
private long[] fibonacciSequence;
@BeforeAll
static void initAll() {
logger.info(() -> "Number of available processors: " + Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
}
@BeforeEach
void init() {
this.fibonacciSequence = new long[SEQUENCE_LENGTH];
fibonacciSequences.add(fibonacciSequence);
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() {
int firstX = 10;
logger.info(() -> "First " + firstX + " numbers: " + Arrays.stream(this.fibonacciSequence)
.limit(firstX)
.mapToObj(Long::toString)
.collect(Collectors.joining(",", "[", ",...]")));
int n = SEQUENCE_LENGTH - 1; // Last number
assertFn(n);
assertFn(n / 2);
assertFn(n / 3);
assertFn(n / 5);
assertFn(n / 10);
assertFn((n / 3) * 2);
assertFn((n / 5) * 4);
}
private void assertFn(int n) {
assertEquals(fibonacciSequence[n - 1] + fibonacciSequence[n - 2], fibonacciSequence[n]);
}
@AfterAll
static void tearDownAll() {
long[] fibonacciSequence = fibonacciSequences.iterator().next();
for (int i = 1; i < fibonacciSequences.size(); i++) {
assertArrayEquals(fibonacciSequence, fibonacciSequences.get(i));
}
}
@Test
@Order(1)
@DisplayName("Calculate Fibonacci sequence sequentially")
public void testSequential() {
logger.info(() -> "Running sequentially. No parallelism");
for (int i = 0; i < fibonacciSequence.length; i++) {
fibonacciSequence[i] = Fibonacci.compute(i);
}
}
@Test
@Order(2)
@DisplayName("Calculate Fibonacci sequence concurrently on all processors")
public void testParallel1() {
testParallel(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
}
@Test
@Order(3)
@DisplayName("Calculate Fibonacci sequence concurrently on half of the processors")
public void testParallel2() {
testParallel(Math.max(1, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() / 2));
}
private void testParallel(int parallelism) {
logger.info(() -> String.format("Running in parallel on %d processors", parallelism));
ThreadExecutor.execute(parallelism, "FibonacciTask", fibonacciSequence,
(long[] fibonacciSequence) -> Arrays.parallelSetAll(fibonacciSequence, Fibonacci::compute)
);
}
static class Fibonacci {
public static long compute(int n) {
if (n <= 1)
return n;
long a = 0, b = 1;
long sum = a + b; // for n == 2
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
a = sum; // using `a` for temporary storage
sum += b;
b = a;
}
return sum;
}
}
}注意testParallel(int parallelism)方法。该方法使用ThreadExecutor实用程序在一个单独的专用线程池上执行并行流,该线程池由提供的线程数组成,其中每个线程被命名为“FibonacciTask”,并与一个序列号连接,例如“FibonacciTask3”。
命名线程来自namedWorkJoinWorkerThreadFactory类。
例如,我用Fibonacci.compute方法中的断点暂停了testParallel2()测试方法,看到6个名为“FibonacciTask1-6”的线程。以下是其中之一:
"FibonacciTask3@2715" prio=5 tid=0x22 nid=NA runnable
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLEat com.github.igalhaddad.threadexecutor.util.ThreadExecutorTests$Fibonacci.compute(ThreadExecutorTests.java:103)
at com.github.igalhaddad.threadexecutor.util.ThreadExecutorTests$$Lambda$366.1484420181.applyAsLong(Unknown Source:-1)
at java.util.Arrays.lambda$parallelSetAll$2(Arrays.java:5408)
at java.util.Arrays$$Lambda$367.864455139.accept(Unknown Source:-1)
at java.util.stream.ForEachOps$ForEachOp$OfInt.accept(ForEachOps.java:204)
at java.util.stream.Streams$RangeIntSpliterator.forEachRemaining(Streams.java:104)
at java.util.Spliterator$OfInt.forEachRemaining(Spliterator.java:699)
at java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.copyInto(AbstractPipeline.java:484)
at java.util.stream.ForEachOps$ForEachTask.compute(ForEachOps.java:290)
at java.util.concurrent.CountedCompleter.exec(CountedCompleter.java:746)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask.doExec(ForkJoinTask.java:290)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool$WorkQueue.topLevelExec(ForkJoinPool.java:1016)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.scan(ForkJoinPool.java:1665)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.runWorker(ForkJoinPool.java:1598)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinWorkerThread.run(ForkJoinWorkerThread.java:177)testParallel(int parallelism)方法执行Arrays.parallelSetAll,这实际上只是一个简单的并行流,如java源代码中实现的:
public static void parallelSetAll(long[] array, IntToLongFunction generator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(generator);
IntStream.range(0, array.length).parallel().forEach(i -> { array[i] = generator.applyAsLong(i); });
}现在让我们看看测试方法:
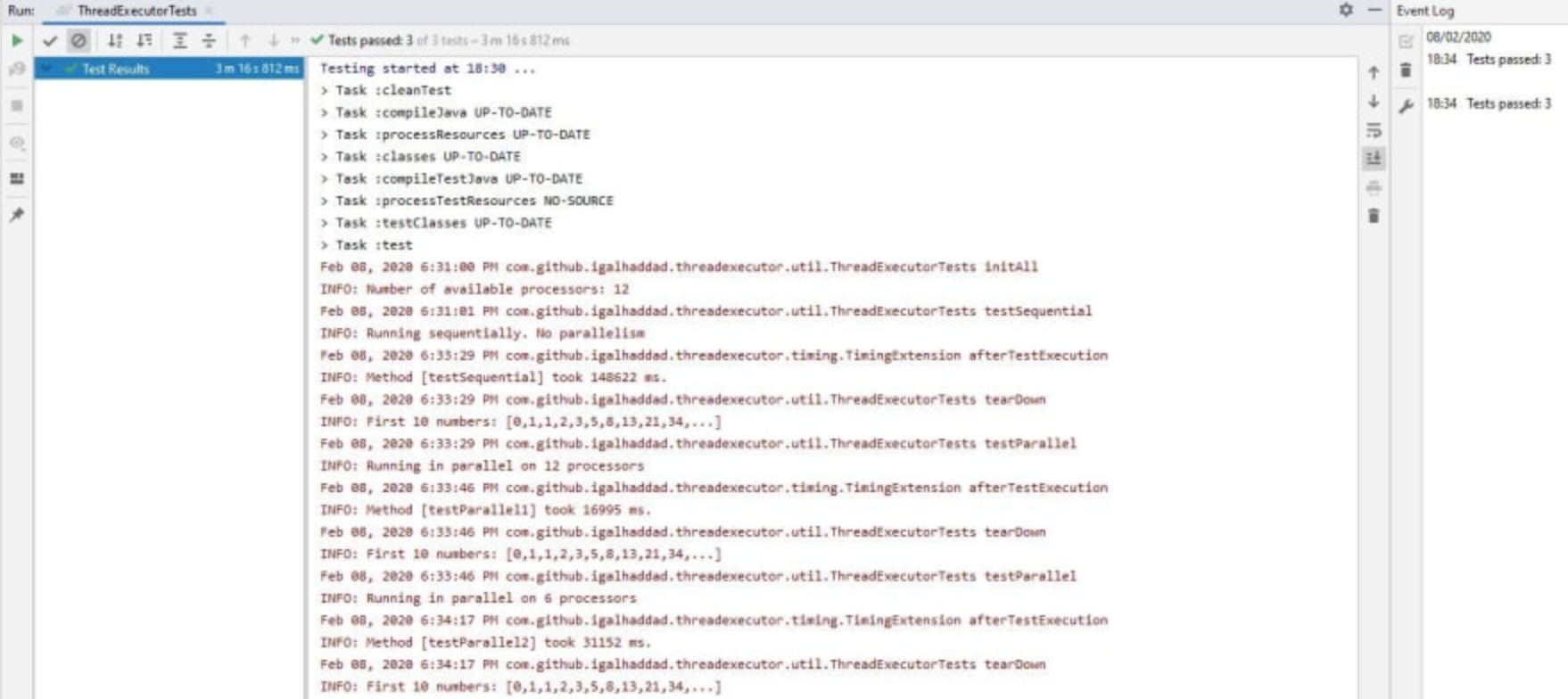
正如您在输出中看到的:
testSequential()测试方法花费了148622毫秒(没有并行性)。testParallel1()测试方法花费了16995ms(12个处理器并行)。testParallel2()测试方法花费了31152毫秒(6个处理器并行)。
所有三种测试方法都完成了同样的任务,即计算长度为1000000个数字的斐波那契序列。
除特别注明外,本站所有文章均为老K的Java博客原创,转载请注明出处来自https://javakk.com/2070.html


 在这个努力程度如此低下的时代,还轮不到比拼天赋。静下心来,just do it
在这个努力程度如此低下的时代,还轮不到比拼天赋。静下心来,just do it

暂无评论