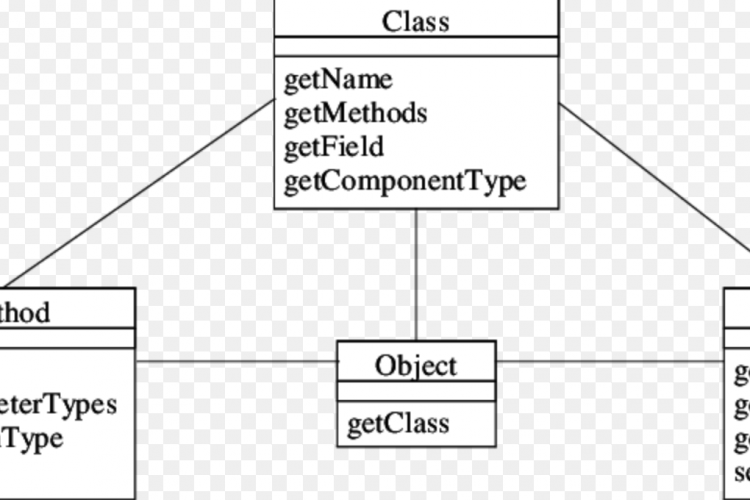
反射是一个API,用于在运行时检查或修改方法、类、接口的行为。
- 下面提供了反射所需的类
java.lang.reflect包裹。 - 反射为我们提供了一个对象所属的类的信息,以及可以使用该对象执行的类的方法的信息。
- 通过反射,我们可以在运行时调用方法,而不管它们使用的访问说明符是什么。
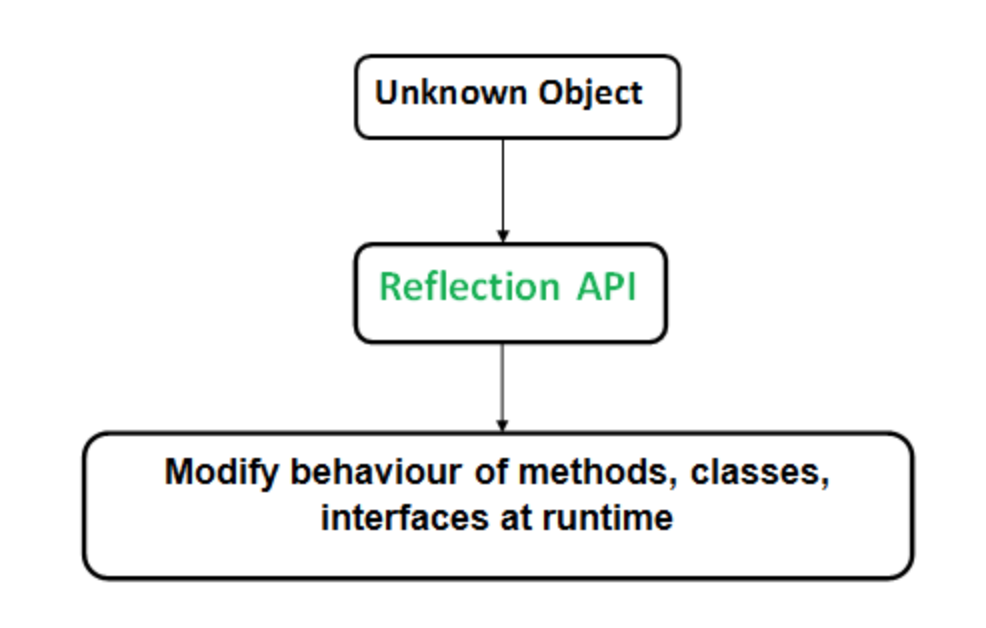
反射可用于获取有关:
- 类Class
getClass()方法用于获取对象所属类的名称。 - 构造函数Constructors
getConstructors()方法用于获取对象所属类的公共构造函数。 - 方法Methods
getMethods()方法用于获取对象所属类的公共方法。
// A simple Java program to demonstrate the use of reflection
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
// class whose object is to be created
class Test
{
// creating a private field
private String s;
// creating a public constructor
public Test() { s = "GeeksforGeeks"; }
// Creating a public method with no arguments
public void method1() {
System.out.println("The string is " + s);
}
// Creating a public method with int as argument
public void method2(int n) {
System.out.println("The number is " + n);
}
// creating a private method
private void method3() {
System.out.println("Private method invoked");
}
}
class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
// Creating object whose property is to be checked
Test obj = new Test();
// Creating class object from the object using
// getclass method
Class cls = obj.getClass();
System.out.println("The name of class is " +
cls.getName());
// Getting the constructor of the class through the
// object of the class
Constructor constructor = cls.getConstructor();
System.out.println("The name of constructor is " +
constructor.getName());
System.out.println("The public methods of class are : ");
// Getting methods of the class through the object
// of the class by using getMethods
Method[] methods = cls.getMethods();
// Printing method names
for (Method method:methods)
System.out.println(method.getName());
// creates object of desired method by providing the
// method name and parameter class as arguments to
// the getDeclaredMethod
Method methodcall1 = cls.getDeclaredMethod("method2",
int.class);
// invokes the method at runtime
methodcall1.invoke(obj, 19);
// creates object of the desired field by providing
// the name of field as argument to the
// getDeclaredField method
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("s");
// allows the object to access the field irrespective
// of the access specifier used with the field
field.setAccessible(true);
// takes object and the new value to be assigned
// to the field as arguments
field.set(obj, "JAVA");
// Creates object of desired method by providing the
// method name as argument to the getDeclaredMethod
Method methodcall2 = cls.getDeclaredMethod("method1");
// invokes the method at runtime
methodcall2.invoke(obj);
// Creates object of the desired method by providing
// the name of method as argument to the
// getDeclaredMethod method
Method methodcall3 = cls.getDeclaredMethod("method3");
// allows the object to access the method irrespective
// of the access specifier used with the method
methodcall3.setAccessible(true);
// invokes the method at runtime
methodcall3.invoke(obj);
}
} 输出结果:
The name of class is Test
The name of constructor is Test
The public methods of class are :
method2
method1
wait
wait
wait
equals
toString
hashCode
getClass
notify
notifyAll
The number is 19
The string is JAVA
Private method invoked重要观察:
如果我们知道方法的名称和参数类型,就可以通过反射调用它。为此,我们使用以下两种方法
getDeclaredMethod():创建要调用的方法的对象。此方法的语法是
Class.getDeclaredMethod(name, parametertype)
name- the name of method whose object is to be created
parametertype - parameter is an array of Class objects
invoke():要在运行时调用类的方法,我们使用以下方法:
Method.invoke(Object, parameter)
If the method of the class doesn’t accepts any
parameter then null is passed as argument.通过反射,我们可以在类对象的帮助下访问类的私有变量和方法,并使用上面讨论的对象调用该方法。为此,我们使用以下两种方法。
Class.getDeclaredField(FieldName):用于获取私有字段。返回指定字段名的字段类型的对象。Field.setAccessible(true):允许访问字段,而与字段一起使用的访问修饰符无关。
使用反射的优点:
- 可扩展性特性:应用程序可以使用外部的、用户定义的类,方法是使用扩展性对象的完全限定名创建实例。
- 调试和测试工具:调试器使用反射属性检查类上的私有成员。
使用反射的缺点:
- 性能开销:反射操作的性能比非反射的操作慢,在性能敏感的应用程序中经常调用的代码部分应该避免。
- 内部公开:反射代码打破了抽象,因此可能会随着平台的升级而改变行为。
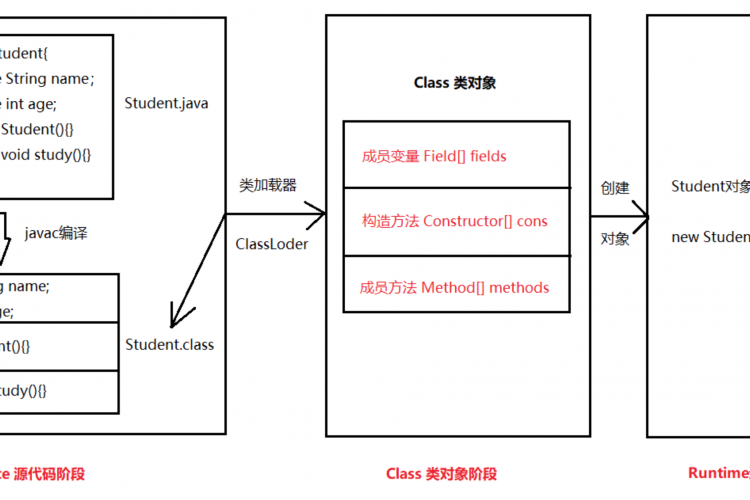
在Java中,反射允许我们在运行时检查和操作类、接口、构造函数、方法和字段。
Java中有一个名为class的类在运行时保存有关对象和类的所有信息。
类的对象描述特定类的属性。此对象用于执行反射。
创建名为class的类的对象
我们可以通过使用class的forName()方法
forName()接受字符串参数(类的名称)并返回类的对象。返回的对象引用字符串指定的类。例如:
Class Dog { }
Class c1 = Class.forName("Dog");使用getClass()方法
getClass()方法使用特定类的对象来创建类的新对象。例如:
Dog d1 = new Dog()
Class c1 = d1.getClass();使用.class
我们还可以使用.Class扩展名创建类的对象。例如:
Class c1 = Dog.class;一旦类的对象被创建,我们就可以使用这些对象来执行反射。
获取接口
我们可以使用类的getInterfaces()方法来收集类实现的接口的信息。此方法返回一个接口数组。
示例:获取接口
import java.lang.Class;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
interface Animal {
public void display();
}
interface Mammal {
public void makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal, Mammal {
public void display() {
System.out.println("I am a dog.");
}
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Bark bark");
}
}
class ReflectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// create an object of Dog class
Dog d1 = new Dog();
// create an object of Class using getClass()
Class obj = d1.getClass();
// find the interfaces implemented by Dog
Class[] objInterface = obj.getInterfaces();
for(Class c : objInterface) {
// print the name of interfaces
System.out.println("Interface Name: " + c.getName());
}
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出:
Interface Name: Animal
Interface Name: Mammal获取超类和访问修改器
类Class的getSuperclass()方法可用于获取有关特定类的超类的信息。
此外,类Class还提供了一个方法getModifier()以整数形式返回类的修饰符。
示例:获取超类和访问修改器
import java.lang.Class;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
interface Animal {
public void display();
}
public class Dog implements Animal {
public void display() {
System.out.println("I am a dog.");
}
}
class ReflectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// create an object of Dog class
Dog d1 = new Dog();
// create an object of Class using getClass()
Class obj = d1.getClass();
// Get the access modifier of Dog in integer form
int modifier = obj.getModifiers();
System.out.println("Modifier: " + Modifier.toString(modifier));
// Find the superclass of Dog
Class superClass = obj.getSuperclass();
System.out.println("Superclass: " + superClass.getName());
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出:
Modifier: public
Superclass: Animal反射字段、方法和构造函数
包java.lang.reflect提供可用于操作类成员的类。例如,
- 方法类-提供有关类中方法的信息
- 字段类-提供有关类中字段的信息
- 构造函数类-提供有关类中构造函数的信息
Field的反射
我们可以使用Field类提供的各种方法检查和修改类的不同字段。
getFields()—返回类及其超类中的所有公共字段getDeclaredFields()—返回类的所有字段getModifier()—以整数形式返回字段的修饰符set(classObject,value)-用指定的值设置字段的值get(classObject)-获取字段的值setAccessible(boolean)-使私有字段可访问
注意:如果我们知道字段的名称,我们可以使用
getField(“fieldName”)—返回类中名为fieldName的公共字段。
getDeclaredField(“fieldName”)—返回类中名为fieldName的字段。
代码示例:访问公共变量field
import java.lang.Class;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
class Dog {
public String type;
}
class ReflectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
Dog d1 = new Dog();
// create an object of the class Class
Class obj = d1.getClass();
// manipulating the public field type of Dog
Field field1 = obj.getField("type");
// set the value of field
field1.set(d1, "labrador");
// get the value of field by converting in String
String typeValue = (String)field1.get(d1);
System.out.println("type: " + typeValue);
// get the access modifier of type
int mod1 = field1.getModifiers();
String modifier1 = Modifier.toString(mod1);
System.out.println("Modifier: " + modifier1);
System.out.println(" ");
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出:
type: labrador
Modifier: public代码示例:访问私有变量field
import java.lang.Class;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
class Dog {
private String color;
}
class ReflectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Dog d1 = new Dog();
// create an object of the class Class
Class obj = d1.getClass();
// accessing the private field
Field field2 = obj.getDeclaredField("color");
// making the private field accessible
field2.setAccessible(true);
// set the value of color
field2.set(d1, "brown");
// get the value of type converting in String
String colorValue = (String)field2.get(d1);
System.out.println("color: " + colorValue);
// get the access modifier of color
int mod2 = field2.getModifiers();
String modifier2 = Modifier.toString(mod2);
System.out.println("modifier: " + modifier2);
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出:
color: brown
modifier: privateJava方法的反射
与字段一样,我们可以使用Method类提供的各种方法检查类的不同方法。
getMethods()—返回类及其超类的所有公共方法getDeclaredMethod()—返回类的所有方法getName()—返回方法的名称getModifiers()—以整数形式返回方法的访问修饰符getReturnType()—返回方法的返回类型
代码示例:
import java.lang.Class;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
class Dog {
public void display() {
System.out.println("I am a dog.");
}
protected void eat() {
System.out.println("I eat dog food.");
}
private void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Bark Bark");
}
}
class ReflectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Dog d1 = new Dog();
// create an object of Class
Class obj = d1.getClass();
// get all the methods using the getDeclaredMethod()
Method[] methods = obj.getDeclaredMethods();
// get the name of methods
for(Method m : methods) {
System.out.println("Method Name: " + m.getName());
// get the access modifier of methods
int modifier = m.getModifiers();
System.out.println("Modifier: " + Modifier.toString(modifier));
// get the return types of method
System.out.println("Return Types: " + m.getReturnType());
System.out.println(" ");
}
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出:
Method Name: display
Modifier: public
Return type: void
Method Name: eat
Modifier: protected
Return Type: void
Method Name: makeSound
Modifier: private
Return Type: void
造函数反射
我们还可以使用构造函数类Constructor提供的各种方法检查类的不同构造函数。
getConstructors()—返回类的所有公共构造函数和类的超类getDeclaredConstructor()—返回所有构造函数getName()—返回构造函数的名称getModifiers()—以整数形式返回构造函数的访问修饰符getParameterCount()—返回构造函数的参数数
import java.lang.Class;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
class Dog {
public Dog() {
}
public Dog(int age) {
}
private Dog(String sound, String type) {
}
}
class ReflectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Dog d1 = new Dog();
Class obj = d1.getClass();
// get all the constructors in a class using getDeclaredConstructor()
Constructor[] constructors = obj.getDeclaredConstructors();
for(Constructor c : constructors) {
// get names of constructors
System.out.println("Constructor Name: " + c.getName());
// get access modifier of constructors
int modifier = c.getModifiers();
System.out.println("Modifier: " + Modifier.toString(modifier));
// get the number of parameters in constructors
System.out.println("Parameters: " + c.getParameterCount());
}
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出:
Constructor Name: Dog
Modifier: public
Parameters: 0
Constructor Name: Dog
Modifier: public
Parameters: 1
Constructor Name: Dog
Modifier: private
Parameters: 2除特别注明外,本站所有文章均为老K的Java博客原创,转载请注明出处来自https://javakk.com/682.html
 在这个努力程度如此低下的时代,还轮不到比拼天赋。静下心来,just do it
在这个努力程度如此低下的时代,还轮不到比拼天赋。静下心来,just do it

暂无评论