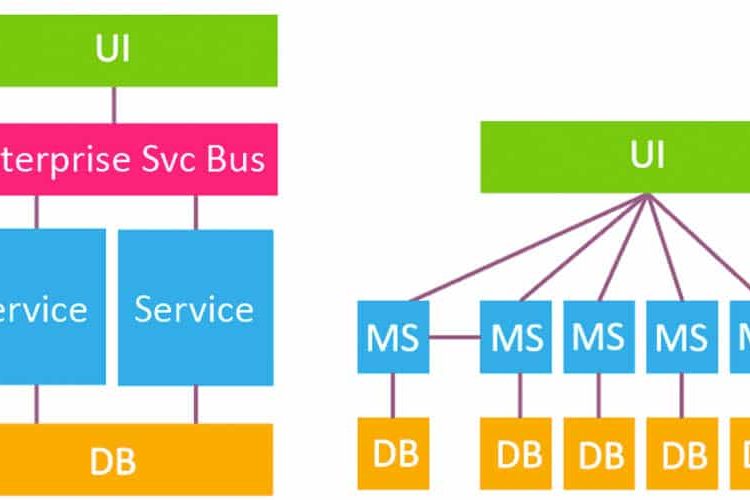
“微服务”用于描述软件体系结构设计,其中许多松散耦合的组件独立运行,但最终作为单个应用程序一起工作。服务通常关注于业务领域或业务实体的特定方面,它们通常使用网络进行通信。
这篇文章是一篇实践性的介绍性指南,介绍如何使用springboot和Netflix开发的软件来构建微服务,以回答这些问题。
Spring Cloud和Netflix OSS
Netflix成为最早采用微服务的公司之一,早在“微服务”一词获得任何吸引力之前,Netflix就已经将其单一的应用程序转变为一种水平可扩展的分布式体系结构。
多年来,作为Netflix开源软件中心(Netflix OSS)项目的一部分,Netflix已经开放了许多工具(他们继续在内部使用)。其中许多工具已经被Spring团队作为Spring Cloud项目的一部分采用,SpringCloud项目提供了一些工具来帮助开发人员在构建分布式系统时使用一些常见的模式。
示例项目
让我们设想一个简单的在线商店场景,在那里客户可以下订单。我们已经可以确定一些我们需要的服务-客户服务和订单服务。我们将一步一步地把每一个都建立起来。
注意:在这个演示中,我们将坚持使用Gradle和springboot2.2.0的Java项目。如果您愿意,可以随意使用Maven或其他受支持的语言。
客户服务
我们从start.spring.io(https://start.spring.io/)创建我们的客户服务项目。这通常是任何新的Spring启动应用程序的最佳起点。如果你看过springdeveloper倡导者和Java冠军joshlong的演讲,我建议你去看,你就会明白为什么这是互联网上第二好的地方!
创建一个带有customer-service的项目,只指定springweb作为依赖项,然后点击Generate下载它。下载并提取后,我们将创建一个Customer类用作域对象:
public class Customer {
private final int id;
private final String name;
public Customer(final int id, final String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}然后,我们将添加一个CustomerController类,该类将公开几个端点,以允许我们按ID查看所有客户和单个客户:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class CustomerController {
private List<Customer> customers = Arrays.asList(
new Customer(1, "Joe Bloggs"),
new Customer(2, "Jane Doe"));
@GetMapping
public List<Customer> getAllCustomers() {
return customers;
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Customer getCustomerById(@PathVariable int id) {
return customers.stream()
.filter(customer -> customer.getId() == id)
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(IllegalArgumentException::new);
}
}数据在这里表示为controller中的一个属性,这是一个坏主意,与实际应用程序完全不同。这不仅意味着给定微服务的每个实例都有自己的数据,而且还忽略了并发性问题,因为Spring中的controller是单例的。实际上,应用程序会有一个外部数据源,并使用类似JPA的东西来连接到它。在这个演示中,我选择保持简单只是为了说明的目的。
最后,让我们配置客户服务,为其提供名称Customer Service和默认端口3001。将以下内容添加到src/main/resources/application.properties文件:
spring.application.name=customer-service
server.port=3001让我们通过使用Gradle构建和运行项目来验证一切正常:
$ cd customer-service
$ ./gradlew bootRun访问http://localhost:3001应显示以JSON表示的客户列表。打开http://localhost:3001/1见Joe Bloggs或http://localhost:3001/2将Jane Doe视为单独的数据项。
订单服务
订单服务的设置实际上与客户服务的设置相同。使用创建具有工件订单服务的项目start.spring.io和以前一样的依赖关系。然后我们可以添加一个Order域对象:
public class Order {
private final int id;
private final int customerId;
private final String name;
public Order(final int id, final int customerId, final String name) {
this.id = id;
this.customerId = customerId;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public int getCustomerId() {
return customerId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}然后创建OrderController来处理端点:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class OrderController {
private final List<Order> orders = Arrays.asList(
new Order(1, 1, "Product A"),
new Order(2, 1, "Product B"),
new Order(3, 2, "Product C"),
new Order(4, 1, "Product D"),
new Order(5, 2, "Product E"));
@GetMapping
public List<Order> getAllOrders() {
return orders;
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Order getOrderById(@PathVariable int id) {
return orders.stream()
.filter(order -> order.getId() == id)
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(IllegalArgumentException::new);
}
}并更新application.properties文件:
spring.application.name=order-service
server.port=3002最后,让我们运行Order服务(./gradlew bootRun)并验证一切正常。
服务发现
微服务架构可以是难以置信的动态。服务不一定有预先知道的固定地址。它们可以移动到不同的端口、机器甚至完全不同的数据中心。通常情况下,一个给定服务会有很多实例——这个数量很少是固定的,因为经常引入新实例来满足需求,当需求减少时就会删除。他们还需要发现其他服务以便与之通信。
Netflix的Eureka是一个服务发现工具,旨在解决这个问题。当一个服务启动时,它向Eureka注册,指定它的名称、地址和其他相关信息。它定期向Eureka发送心跳消息,以告知它仍然处于活动状态并且能够处理请求。如果心跳因任何原因停止,Eureka将在配置的超时后取消注册该特定服务。服务还可以向Eureka请求注册表信息,以便发现其他服务。

使用创建新项目start.spring.io(https://start.spring.io/)发现服务的组件。选择Eureka服务器作为其唯一依赖项,然后单击Generate。打开DiscoveryServiceApplication类并添加@enableurekaserver注释,以建立Eureka服务注册表:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class DiscoveryServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DiscoveryServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}默认情况下,为了提供高可用性,Eureka服务器与对等方通信以共享其注册表信息,但是由于我们只在这里运行一个实例,所以让我们禁用该功能并将服务配置为不向对等方注册,也不获取对等方注册表。我们还将给它一个名称和默认端口3000(Eureka的默认端口是8761)。在应用程序属性添加以下内容:
spring.application.name=discovery-service
server.port=3000
eureka.client.registerWithEureka=false
eureka.client.fetchRegistry=false
eureka.instance.hostname=localhost
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/构建并运行服务(./gradlew bootRun),并通过访问http://localhost:3000. 您应该看到一个Eureka仪表板,其中显示有关正在运行的实例的信息:

向发现服务注册
现在我们的发现服务已经启动并运行,我们的域服务必须与它通信以注册自己并接收注册表更新。为此,我们需要将Eureka发现客户机依赖项添加到我们的项目中。通常,向Gradle项目添加依赖项就像向项目的dependencies块添加一行一样简单build.gradle文件。但是,在这种情况下最好使用start.spring.io(https://start.spring.io/)再生我们的生命build.gradle文件,因为它可以有点棘手。一旦生成,我们的build.gradle文件将如下所示:
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.2.0.RELEASE'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.0.8.RELEASE'
id 'java'
}
group = 'com.github.jrhenderson1988'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = '1.8'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
maven { url 'https://repo.spring.io/milestone' }
}
ext {
set('springCloudVersion', "Hoxton.RC1")
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client'
testImplementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test') {
exclude group: 'org.junit.vintage', module: 'junit-vintage-engine'
}
}
dependencyManagement {
imports {
mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}"
}
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}现在,让我们用@enableurekaclient注释来注释CustomerServiceApplication和OrderServiceApplication类:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class CustomerServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CustomerServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}最后,让我们告诉Eureka客户在哪里可以找到我们的发现服务。在每个服务的应用程序属性,添加以下行:
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:3000/eureka/启动发现服务,然后启动客户服务和订单服务应用程序,然后打开发现服务的Eureka仪表板—您应该看到这两个服务都已注册。

使用Zuul实现路由和服务器端负载平衡
在微服务体系结构中,可以有数十个、数百个甚至数千个服务。许多是私人和内部的,但有些需要暴露在外面的世界。我们需要一个单一的进入系统的入口点,以允许我们连接选定的服务并将其暴露给外部世界。
Netflix的Zuul是一个基于JVM的路由器和服务器端负载均衡器。通过配置将路由映射到服务,Zuul可以与Eureka集成,以发现服务位置以实现负载平衡,并向它们发送代理请求。
Zuul还支持过滤器,允许开发人员在将请求发送到服务(预过滤器)之前拦截请求,并在将响应发送回客户端(后过滤器)之前拦截响应。这使开发人员能够实现所有服务通用的功能,在处理请求之前或之后运行。过滤器通常用于身份验证、负载削减和CORS管理等功能。

网关服务
回到start.spring.io(https://start.spring.io/),以Zuul和Eureka Discovery Client作为依赖项,使用Artifact gateway服务创建一个新项目。生成后,打开GatewayServiceApplication类并添加@EnableZuulProxy和@enableurekaclient注释。
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.EnableZuulProxy;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableZuulProxy
@EnableEurekaClient
public class GatewayServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GatewayServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}现在将以下内容添加到应用程序属性:
spring.application.name=gateway-service
server.port=80
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:3000/eureka/
zuul.routes.customers.path=/customers/**
zuul.routes.customers.serviceId=customer-service
zuul.routes.orders.path=/orders/**
zuul.routes.orders.serviceId=order-service
我们给了这个项目一个网关服务的名称,将它设置为在端口80上运行(这是HTTP的默认值),并告诉它在端口3000上找到我们的发现服务。我们还添加了一些路由映射,这样对/customers/**和/orders/**的请求将分别转发到名为customer service和order service的服务。Zuul使用发现服务提供的服务注册表来定位每个目标服务。
使用Gradle(./gradlew bootRun),启动发现服务,然后启动客户服务、订单服务和网关服务:
一旦一切都在运行,请等待几分钟,以便发现服务从每个服务接收连接,并将其注册表传播回每个应用程序。
访问http://localhost/customers。您应该看到与以前相同的客户JSON表示。实际上,客户服务应该还在运行。试着打http://localhost/orders也要看订单。
小结
让我们看看系统中当前发生的情况:
- 必须首先启动发现服务。当它加载时,它处于空闲状态,等待传入的连接。
- 在启动时,其他服务与发现服务通信以注册它们自己并计划发送一个常规心跳信号。他们还定期向发现服务请求注册信息,发现服务会给出所有注册服务的详细信息。
- 当请求被发送到网关服务时,它会检查其映射的路由是否匹配。如果找到目标服务,它将在本地注册表中查找从发现服务检索到的目标服务的名称,以计算出目标服务的物理地址,然后将传入的请求代理给它。
- 目标服务处理传入的请求并响应网关服务,然后网关服务响应客户端。
完整源码地址:https://github.com/jrhenderson1988/building-microservices-with-spring-boot/tree/part-1
除特别注明外,本站所有文章均为老K的Java博客原创,转载请注明出处来自https://javakk.com/1801.html

 在这个努力程度如此低下的时代,还轮不到比拼天赋。静下心来,just do it
在这个努力程度如此低下的时代,还轮不到比拼天赋。静下心来,just do it

暂无评论